In Excel, the TEXT function performs two operations:
- converts a number to text,
- at the same time, formats that number in a specified way.
The TEXT function syntax is as follows:
= TEXT ( value ; “format_text” )
Value can be any number, either inputted into the function or referenced.
Format text nested inside quotation marks is based on the number format codes used in Excel.
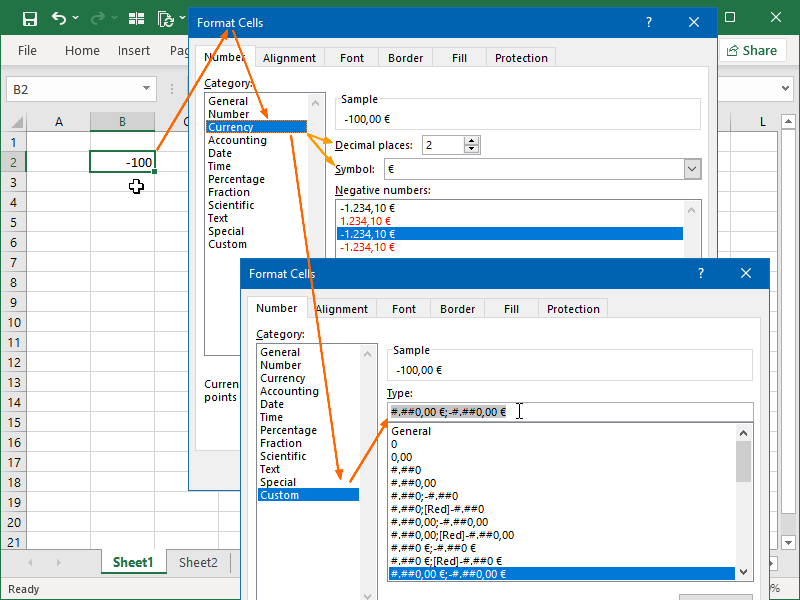
Excel number format codes can be copied from the Format Cells pop-up:
That copied number format code can be used as format text in the TEXT function arguments:
A custom number format code can also be coded.
As is typical with custom number format codes, all sections of the code don’t have to be specified, and if only the first section of the format code is specified, it is used for both positive and negative numbers.
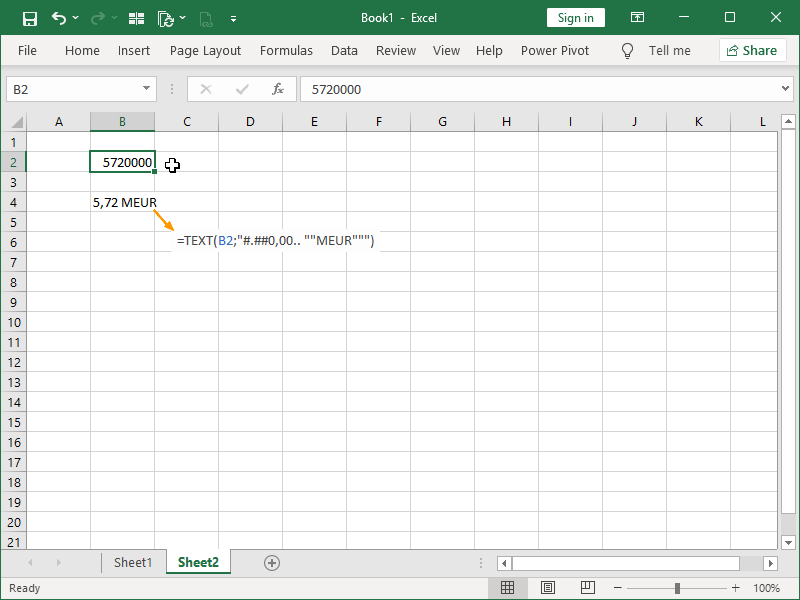
In the following example, we will format our output as millions, also adding the “MEUR” text:
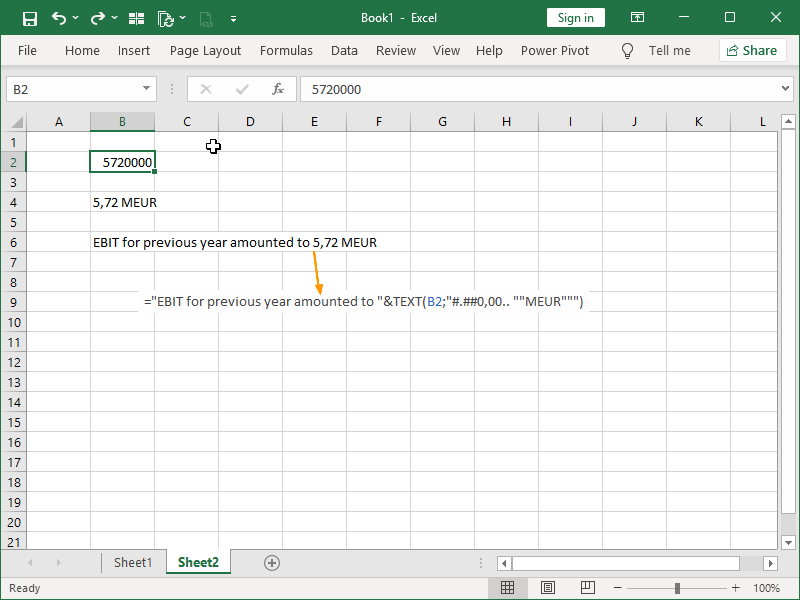
The TEXT function is often used for concatenation, i.e., joining values together to create a new text string. For example, it can be used to format a value and append it to another text string:
The question mark (which adds spaces for non-significant zeros) and character for zero (which displays non-significant zeros) are often used in order to return some common items.
Here, we will return a number formatted as text, a number formatted as text that contains digit groups separated by a minus sign, and a number formatted as text that contains leading zeros:
Date format codes can also be copied from the Format Cells pop-up:
The TEXT function will be particularly useful here: as dates are stored as decimal numbers in Excel, that numerical value must be formatted in order to be useful in any way.
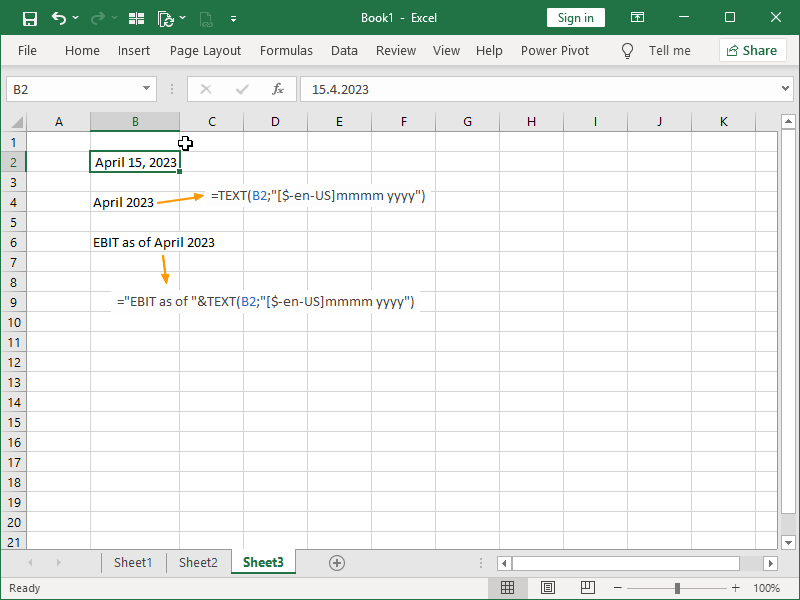
In order to improve or customize the presentation of date and time, custom date formats can also be used:
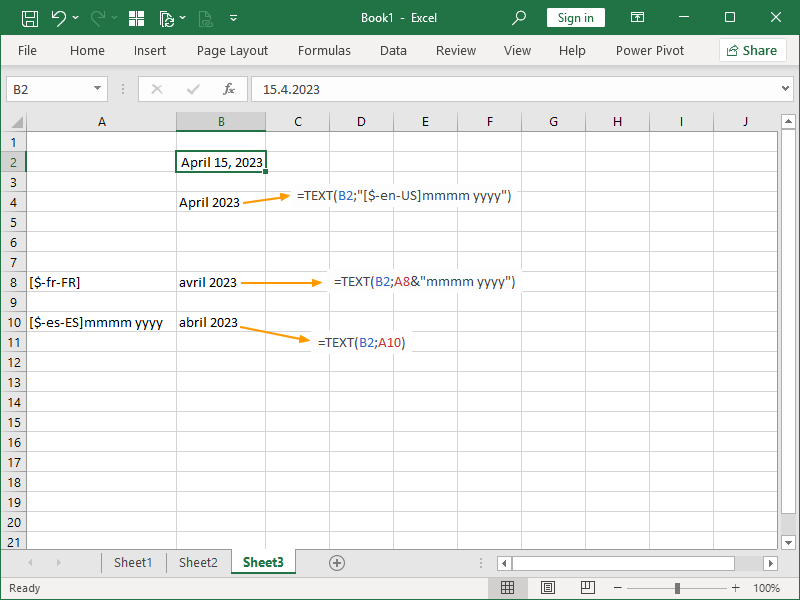
Note the usage of location codes in date format codes. Those are used if we want to display time in a language different from our localization of Excel or if we need to ensure that our return will stay consistent even if a user in a different location receives our workbook.
For a detailed list of the available locales, you can check under the Format Cells, Date and/or Time format category.
Finally, if we don’t want our format text to be hardcoded, that part of the argument can be referred to or concatenated:
Dig deeper:




7 thoughts on “TEXT function”